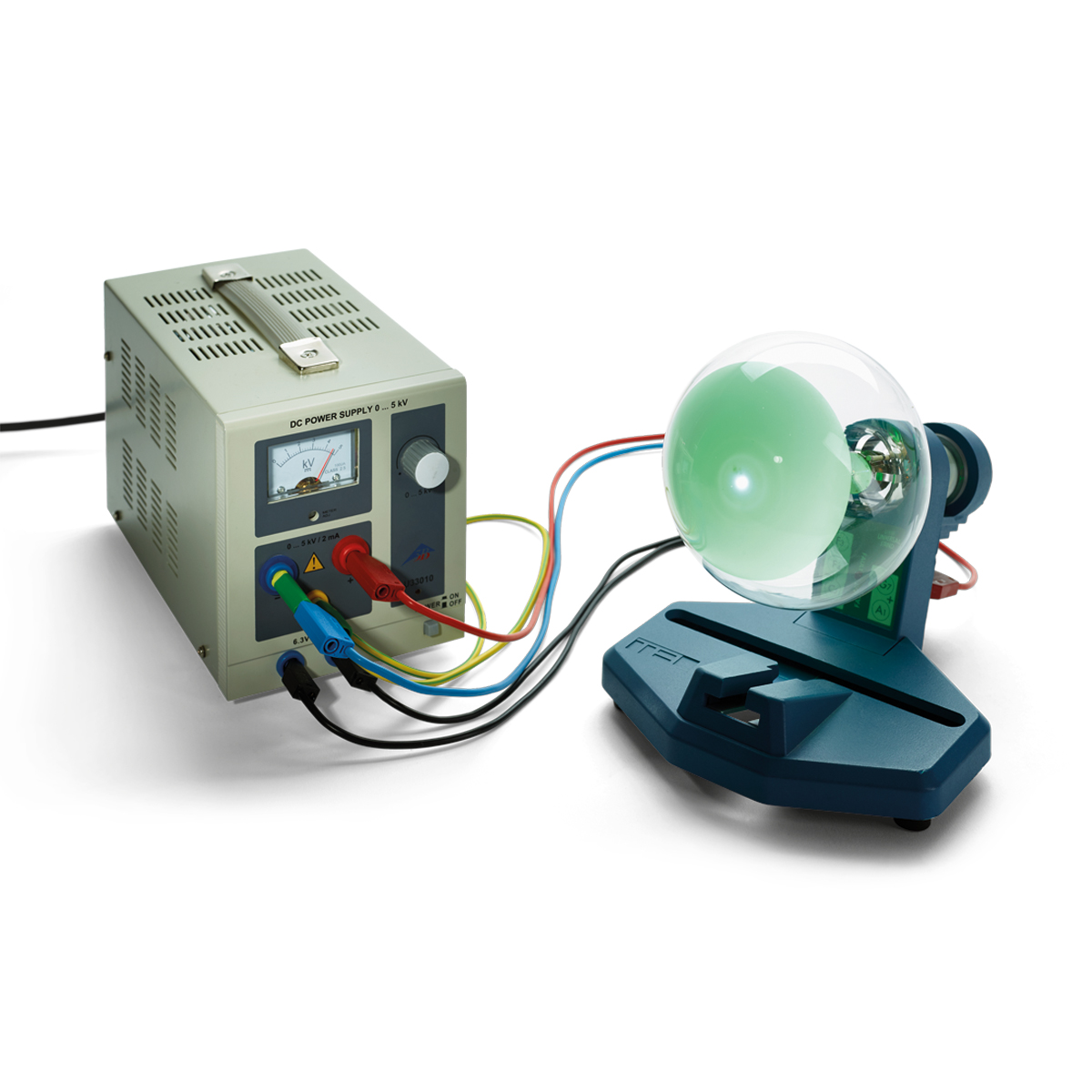
Principle
Fast electrons are diffracted from a polycrystalline layer of graphite: interference rings appear on a fluorescent screen. The interplanar spacing in graphite is determined from the diameter of the rings and the accelerating voltage.
Benefits
- Experience the essence of the Nobel Prize: de Broglie (1929)
- Impressive visualization of a Nobel Prize experiment with various changeable parameters
- Simple setup
- Easy determination of the interplanar spacing of graphite
- Perfect demonstration of wave-particle duality
Tasks
- To measure the diameter of the two smallest diffraction rings at different anode voltages.
- To calculate the wavelength of the electrons from the anode voltages.
- To determine the interplanar spacing of graphite from the relationship between the radius of the diffraction rings and the wavelength.
Learning objectives
- Bragg reflection
- Debye-Scherrer method
- Lattice planes
- Graphite structure
- Material waves
- De Broglie equation