setTimeout(function(){
window.print();
},500)

Technical data Electron diffractionArticle no: P2511301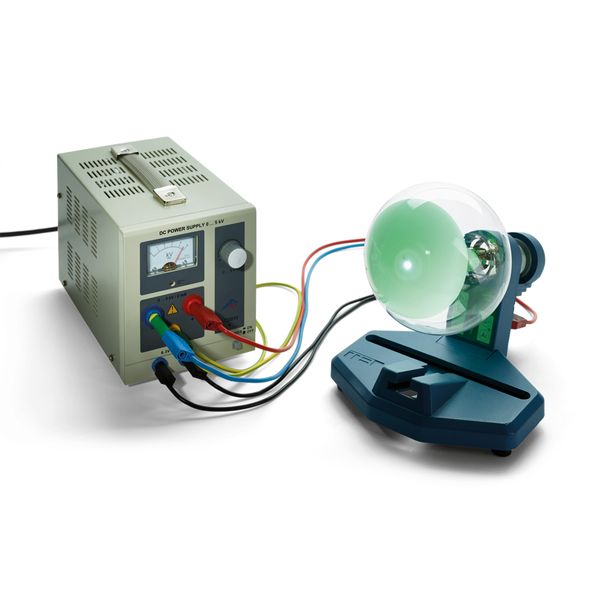  Principle Fast electrons are diffracted from a polycrystalline layer of graphite: interference rings appear on a fluorescent screen. The interplanar spacing in graphite is determined from the diameter of the rings and the accelerating voltage. Benefits
Tasks
Learning objectives
Scope of delivery
| ||||||||||||
PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG
Robert-Bosch-Breite 10 – 37079 Göttingen – Germany
www.phywe.com
Robert-Bosch-Breite 10 – 37079 Göttingen – Germany
www.phywe.com