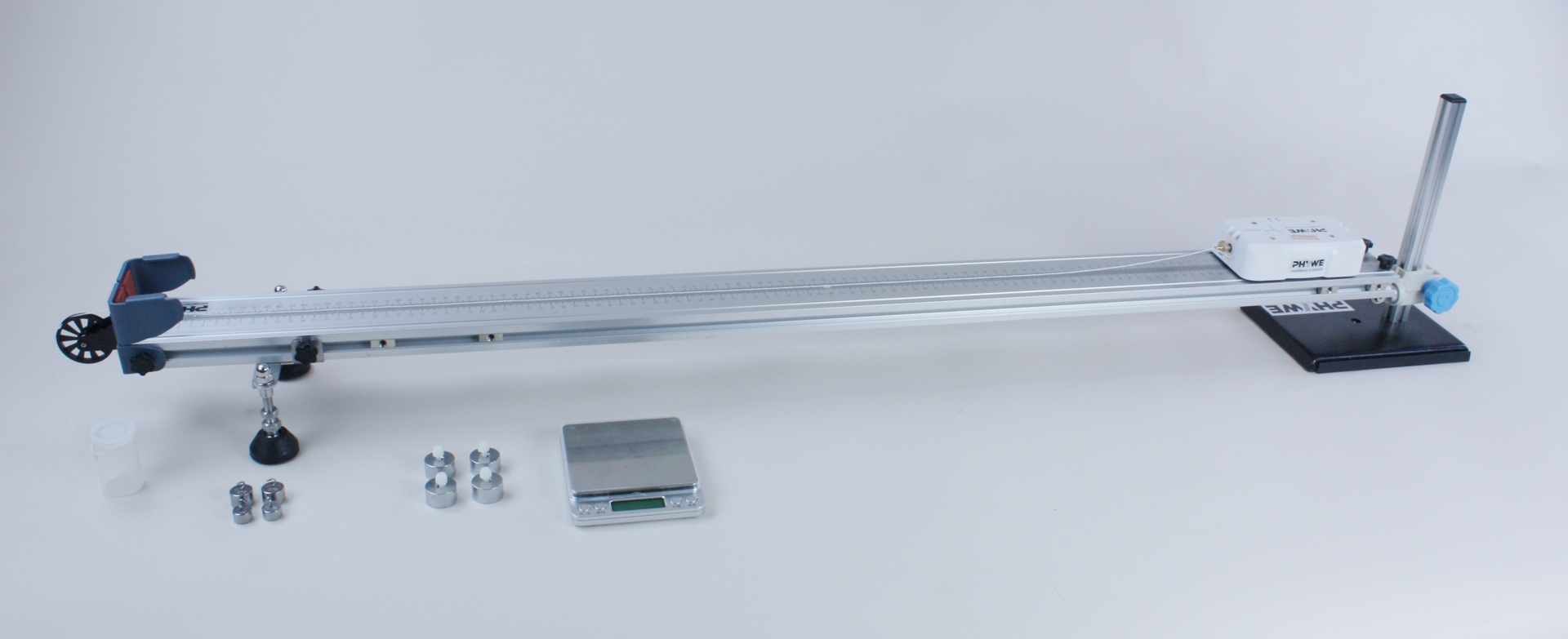
Principle
Acceleration is one of the basic concepts of the theory of motion. It indicates how fast an object changes its speed and is measured in the unit m/s². The concept of acceleration is based on the average acceleration as the quotient of the change in speed in a given period of time. According to Newton's second law, the force in a motion with constant mass can be determined as the product of mass and acceleration.
Benefits
- Free measuring software DigiCartAPP for all mobile devices and all operating systems (Windows, Android, iOS).
- Especially understandable and didactically prepared test description can be called up in the DigiCartAPP.
- Complete evaluation function for the measured data directly in the DigiCartAPP.
- DigiCart:
- Long-life lithium-ion batteries with charge protection function
- Transmission of measurement data via Bluetooth 4.0
- Integrated sensors (force, speed, acceleration and position sensor)
- Digital measured value acquisition:
- Future-oriented teaching: Integration into digital science teaching with tablets or smartphones.
- Increased student motivation by using the intuitive DigiCartAPP.
- Increase of media competence.
Tasks
1) With a constant mass of the DigiCart, use the DigiCart App to record force-time and speed-time diagrams for different forces. Use these to analyze the relationship between force and acceleration.
2) At constant force and variable mass of the DigiCart, record force-time and speed-time diagrams. Analyze the relationship between acceleration and mass.
Learning Objectives
In this experiment the students learn about the physical relationship between force and acceleration. This relationship is expressed physically in Newton's second law.