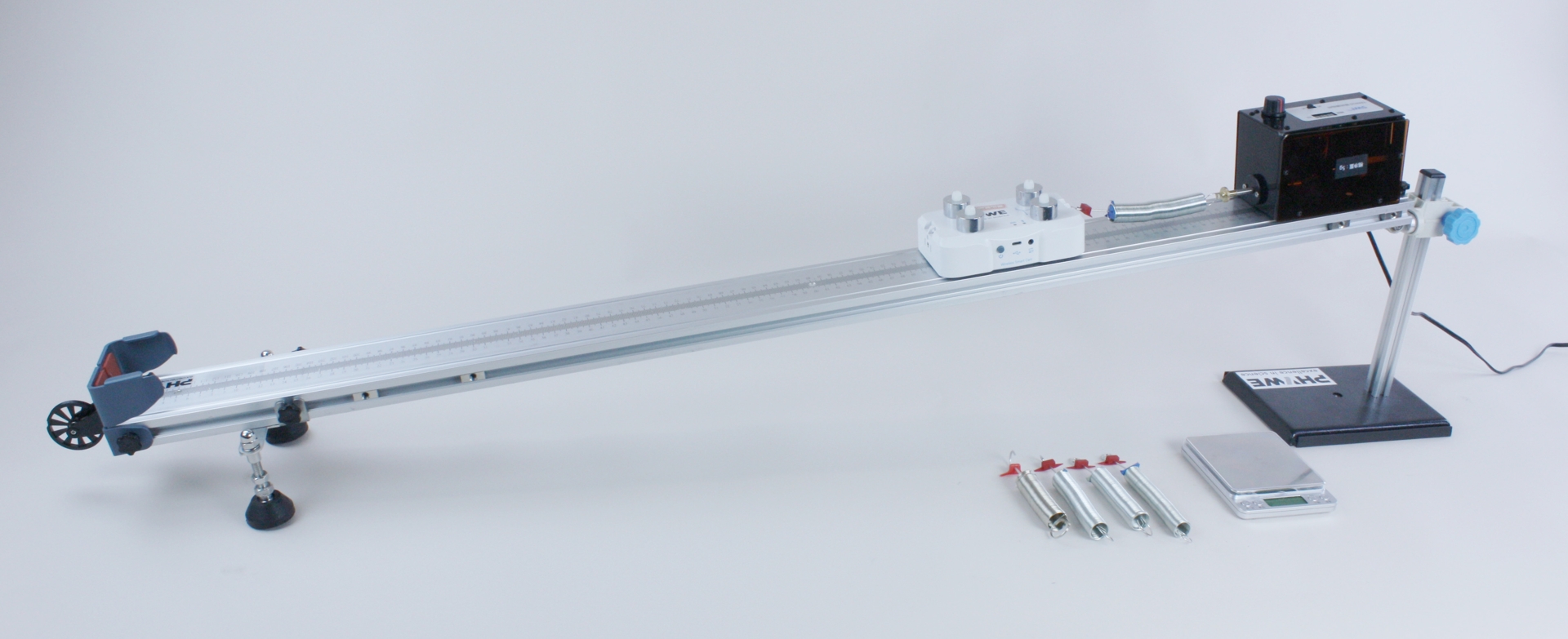
Principle
Oscillations are repeated temporal fluctuations of state variables of a system. Oscillations can be characterized by the specification of amplitude and frequency. The amplitude describes the extent of the oscillation from a defined rest position. The frequency indicates how many oscillations the system performs in one second. The frequency is the reciprocal value of the period duration of an oscillation.
Forced oscillation: For forced oscillation, an external frequency is forced upon the system. A mechanical mass-spring-system shall serve as an example.
Benefits
- Free measuring software DigiCartAPP for all mobile devices and all operating systems (Windows, Android, iOS).
- Especially understandable and didactically prepared test description can be called up in the DigiCartAPP.
- Complete evaluation function for the measured data directly in the DigiCartAPP.
- DigiCart:
- Long-life lithium-ion batteries with charge protection function
- Transmission of measurement data via Bluetooth 4.0
- Integrated sensors (force, speed, acceleration and position sensor)
- Digital measured value acquisition:
- Future-oriented teaching: Integration into digital science teaching with tablets or smartphones.
- Increased student motivation by using the intuitive DigiCartAPP.
- Increase of media competence.
Tasks
1) Examine qualitatively the amplitude behaviour as a function of the excitation frequency.
2) Investigate quantitatively the dependence of the resonance frequency on the mass.
Learning Objectives
In this experiment the students learn about the behaviour of forced vibrations. The dependence of the resonance frequency on the mass is investigated.