setTimeout(function(){
window.print();
},500)

Technical data Stern-Gerlach experimentArticle no: P2511101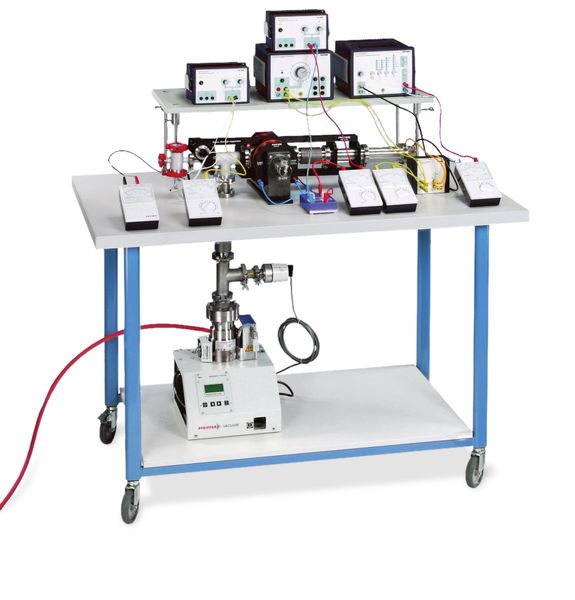   Principle A beam of potassium atoms generated in a hot furnace travels along a specific path in a magnetic two-wire field. Because of the magnetic moment of the potassium atoms, the non-homogeneity of the field applies a force at right angles to the direction of their motion. The potassium atoms are thereby deflected from their path. By measuring the density of the beam of particles in a plane of detection lying behind the magnetic field, it is possible to draw conclusions as to the magnitude and direction of the magnetic moment of the potassium atoms. Benefits
Tasks
Learning objectives
Scope of delivery
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG
Robert-Bosch-Breite 10 – 37079 Göttingen – Germany
www.phywe.com
Robert-Bosch-Breite 10 – 37079 Göttingen – Germany
www.phywe.com