Liver cells (hepatocytes) 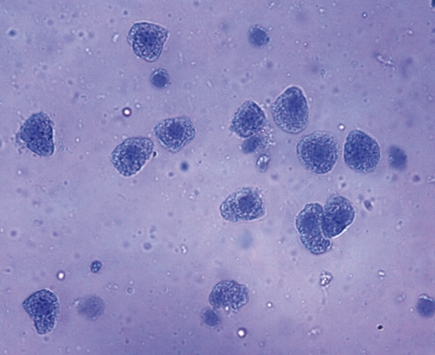  Principle
The liver is the central organ of human and animal metabolism. It influences, for example, the blood sugar level, synthesizes various blood proteins, and decomposes toxic metabolic products and other toxicants taken up with the food. The bile which the liver produces accumulates in the gallbladder and is discharged into the intestines when needed. It emulsifies dietary fat. The human liver is a very large organ weighing approx. 1,500 g and lies on the right side of the abdomen, directly under the diaphragm.
Benefits - Experiment is part of a complete solution set with a total of 50 experiments for all microscopy applications
- With student worksheet, appropriate for all class levels
- With detailed instructor information, incl. sample microscopy image
- Optimized for tight schedules, i.e. minimum preparation time required
- Microscopy solution set specifically designed to include all required accessories
- Content available with matching multimedia files
Tasks - Examine the shape of individual liver cells and compare their structure with a plant cell.
Learning objectives - Liver
- Liver cells
- Metabolism
- Blood sugar level
- Blood proteins
Scope of delivery |
PHYWE Binocular student microscope, 1000x, mechanical stage
|
MIC-129A
|
1
| |
Microscopic slides, 50 pcs
|
64691-00
|
1
| |
Cover glasses 18x18 mm, 50 pcs
|
64685-00
|
1
| |
Scissors,straight,pointed,l 110mm
|
64623-00
|
1
| |
Beaker, 100 ml, plastic (PP)
|
36011-01
|
1
| |
Tweezers,straight,pointed,120mm
|
64607-00
|
1
| |
Scalpel holder
|
64615-00
|
1
| |
Scalpel blades,rounded tip,10 off
|
64615-02
|
1
| |
Glass rod, boro 3.3, l=200mm, d=5mm
|
40485-03
|
1
| |
Chemicals set for TESS advanced Microscopy
|
13290-10
|
1
|
|