Technical data Diffraction at a narrow obstacle with laserArticle no: P1195601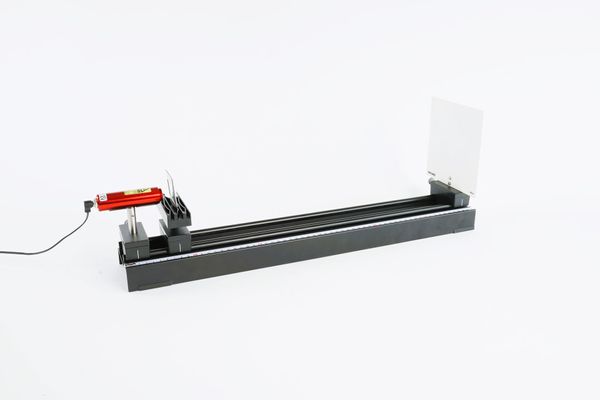 
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
Principle In this experiment the students should come to realize that in
the shadow area behind a narrow obstacle regular patterns of
brightness will be found which are formed by diffraction at the
edges of the obstacle. By comparing the diffraction pattern with
that created by diffraction at a slit having the same width as the
obstacle, they should gain an understanding of
Babinet's Principle and find it confirmed. Benefits
Tasks What sort of shadow is created behind a narrow obstacle? Direct a narrow pencil of light onto a slender obstacle so that part of the beam grazes the side. Observe the shadow thus created and compare it with the diffraction pattern formed when the light beam strikes a slit of the same width as the obstacle. Scope of delivery
| ||||||||||||||||||
Robert-Bosch-Breite 10 – 37079 Göttingen – Germany
www.phywe.com