setTimeout(function(){
window.print();
},500)

Technical data Temperature behaviour of organic compoundsArticle no: P1149800 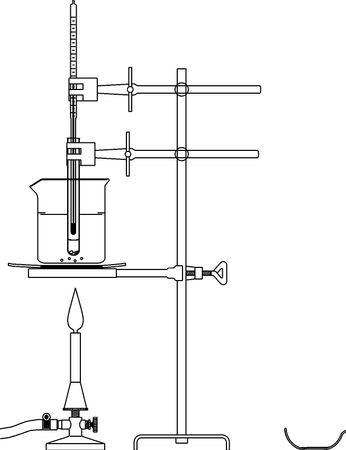 Principle Organic compounds always contain the element carbon and the carbon atoms are combined with other carbon atoms or atoms of other elements by covalent bonds. . This is the reason why the C-C or C-H bonds are stable at normal (room) temperature. However low heat resistance is characteristic for many organic compounds. These compounds burn or carbonize when heated over a few hundred degrees Celsius. The thermal stability of organic compounds, which is low in comparison to many salts and metals, is a result of the low polar character of C-C and C-H bonds. In this experiment the students investigate the temperature behavior of molecular (organic) substances.
Learning objectives
Scope of delivery
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG
Robert-Bosch-Breite 10 – 37079 Göttingen – Germany
www.phywe.com
Robert-Bosch-Breite 10 – 37079 Göttingen – Germany
www.phywe.com