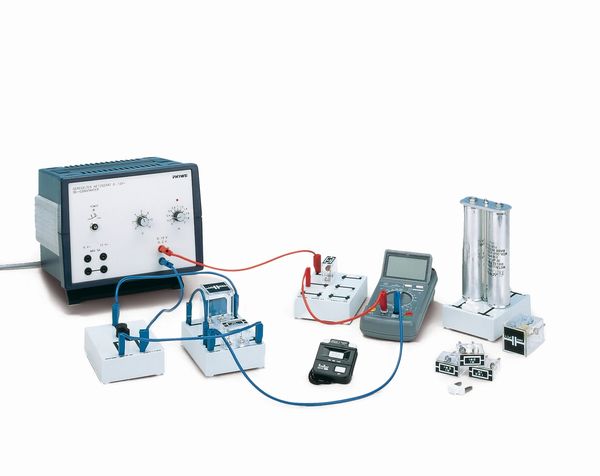
Charging curve of a capacitor / charging and discharging of a capacitor Principle A capacitor is charged by way of a resistor. The current is measured as a function of time and the effects of capacitance, resistance and the voltage applied are determined. Benefits - Simple and very clear set-up: only few components required
- Further experiments in electricity and electronics can be performed with the equipment
Tasks - To measure the charging current over time:
- using different capacitance values C, with constant voltage U and constant resistance R
- using different resistance values (C and U constant)
- using different voltages (R and C constant).
- To determine the equation representing the current when a capacitor is being charged, from the values measured.
Learning objectives - Charging
- Discharging
- Time constant
- Exponential function
- Half life
Even more accurate readings are possible when using the multimeter 07124-12. Scope of delivery |
Connection box
|
06000-00
|
2
| |
Two-way switch, single pole
|
06005-00
|
1
| |
Capacitor, 2 x 30 µF
|
06007-00
|
1
| |
Resistor 100 Ohm, 1W, G1
|
39104-63
|
1
| |
Resistor 1 MOhm, 1W, G1
|
39104-52
|
4
| |
brigde plug
|
06027-07
|
2
| |
Capacitor 1 microF/ 100V, G2
|
39113-01
|
1
| |
Capacitor 4,7microF/ 100V, G2
|
39113-03
|
1
| |
PHYWE Power supply, 230 V, DC: 0...12 V, 2 A / AC: 6 V, 12 V, 5 A
|
13506-93
|
1
| |
Digital stopwatch, 24 h, 1/100 s and 1 s
|
24025-00
|
1
| |
Digital multimeter, 600V AC/DC, 10A DC, 20MΩ
|
07124-12
|
1
| |
Connecting cable, 32 A, red, various lengths
|
07360-01
|
3
| |
Connecting cable, 32 A, blue, various lengths
|
07360-04
|
4
|
|