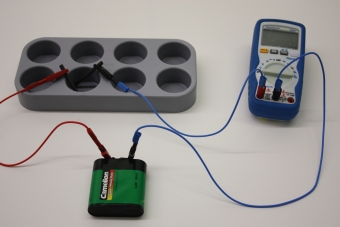
Galvanic zincking Principle Technically, corrosion protection by zincking is attained by two different processes: By hot galvanizing, or by electroplating, i.e. by galvanic (electrochemical) deposition of zinc from a solution of zinc, in which the iron object to be treated is hung as the cathode. The electroplating procedure consumes considerably less zinc per square meter of surface than hot galvanizing, and is therefore now the preferred procedure.
In this experiment, a piece of sheet iron is coated electrochemically with zinc, and subsequently a long term experiment is carried out to demonstrate the protective action of this zincking against corrosion. Learning objectives - Principle of galvanic zincking as corrosion protection
Benefits - Easy teaching and efficient learning by using interactive experimentation PHYWE-Software
- Experiment is part of a complete solution set with experiments for the topic Electrochemistry matched with international curriculum: all topics are covered
Scope of delivery |
PHYWE Digital multimeter, 600V AC/DC, 10A AC/DC, 20 MΩ, 200 µF, 20 kHz, −20°C…760°C
|
07122-00
|
1
| |
Connecting cord, 2 mm-plug, 5A, 500 mm, red
|
07356-01
|
1
| |
Connecting cord, 2 mm-plug, 5A, 500 mm, blue
|
07356-04
|
2
| |
Reducing plug 4mm/2mm socket, 2
|
11620-27
|
2
| |
Alligator clip, insulated, 2 mm socket, 2 pcs.
|
07275-00
|
1
| |
Set Strip electrode (Al, Fe, Pb, Zn, Cu)
|
07856-00
|
2
| |
Emery paper, medium
|
01605-00
|
1
| |
Block with 8 holes, d = 40 mm
|
37682-00
|
1
| |
Sheet metal strips, 20 pcs
|
06532-00
|
1
| |
Zinc sulphate 7-hydr. 250 g
|
30249-25
|
1
| |
Zinc chloride, dry, 250 g
|
31983-25
|
1
| |
Sodium sulphate dried 250 g
|
48344-25
|
1
| |
Sulphuric acid,0.5M 1000 ml
|
48462-70
|
1
|
|