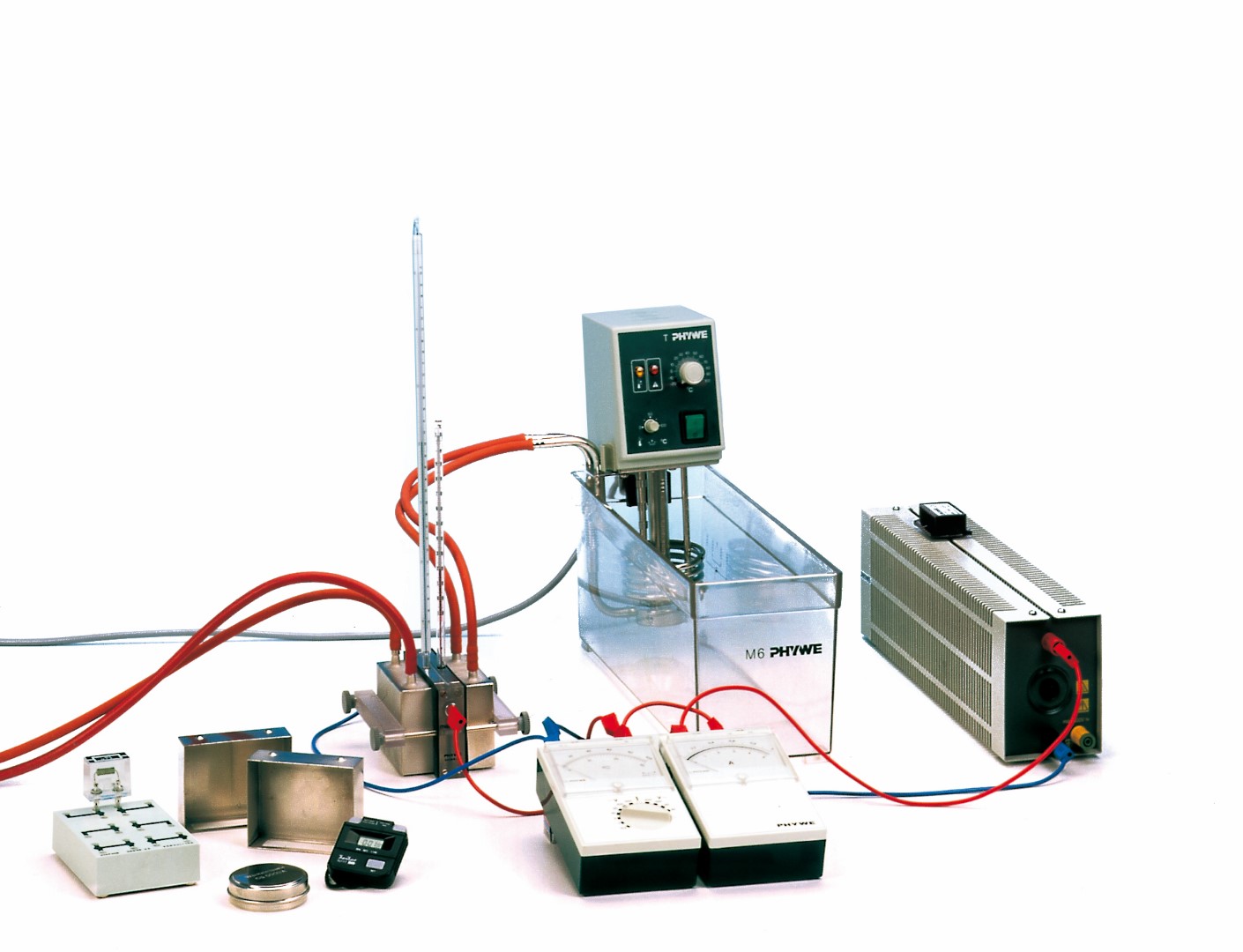
Principle
In a semi-conductor thermogenerator, the no-load voltage and the short-circuit current are measured as a function of the temperature difference. The internal resistance, the Seebeck coefficient and the efficiency are determined.
Benefits
- Open design allows to fully understand function and applications
- Individual instruments for distinct functions (no "black box")
- Key products of the experiment setup can also be used for investigating the Peltier effect
Tasks
- To measure no-load voltage U0 and short-circuit current Is at different temperature differences and to determine the Seebeck coefficient.
- To measure current and voltage at a constant temperature difference but with different load resistors, and to determine the internal resistance Ri from the measured values.
- To determine the efficiency of energy conversion, from the quantity of heat consumed and the electrical energy produced per unit time.
Learning objectives
- Seebeck effect (thermoelectric effect)
- Thermoelectric e.m.f.
- Efficiency
- Peltier coefficient
- Thomson coefficient
- Seebeck coefficient
- Direct energy conversion
- Thomson equations