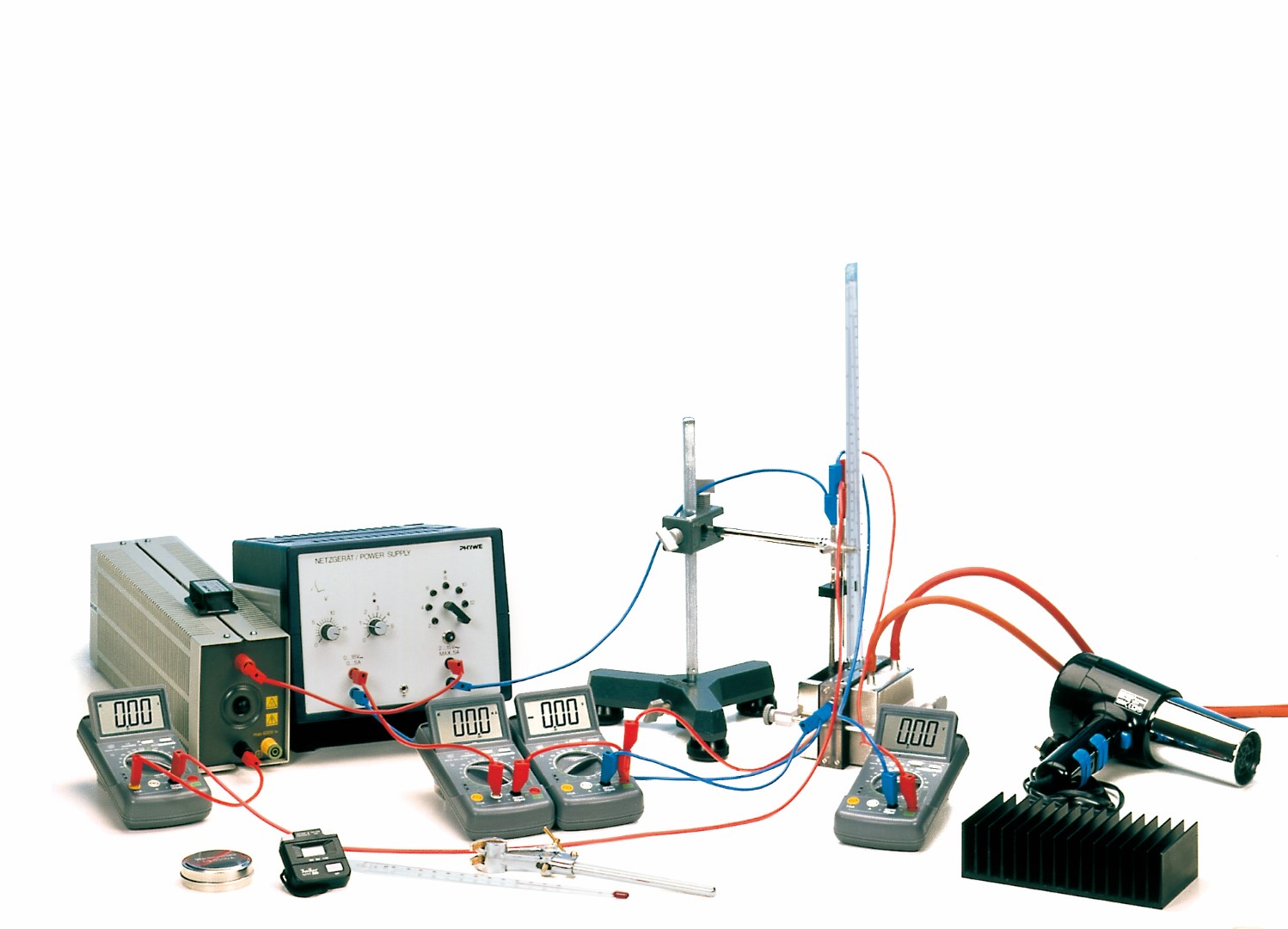
Principle
As well as the cooling and the heating capacity and efficiency rating of a Peltier heat pump are determined under different operating conditions.
Benefits
- Open design allows to fully understand function and applications
- Individual instruments for distinct functions (no "black box")
- Key products of the experiment setup can also be used for investigating the Seebeck effect
Tasks
- To determine the cooling capacity Pc of the pump as a function of the current and to calculate the efficiency rating hc at maximum output.
- To determine the heating capacity Pw of the pump and its efficiency rating hw at constant current and constant temperature on the cold side.
- To determine Pw, ηw and Pc , ηc from the relationship between temperature and time on the hot and cold sides.
- To investigate the temperature behaviour when the pump is used for cooling, with the hot side air-cooled.
Learning objectives
- Peltier effect
- Heat pipe
- Thermoelectric e. m. f.
- Peltier coefficient
- Cooling capacity
- Heating capacity
- Efficiency rating
- Thomson coefficient
- Seebeck coefficient
- Thomson equations
- Heat conduction
- Convection
- Forced cooling
- Joule effect