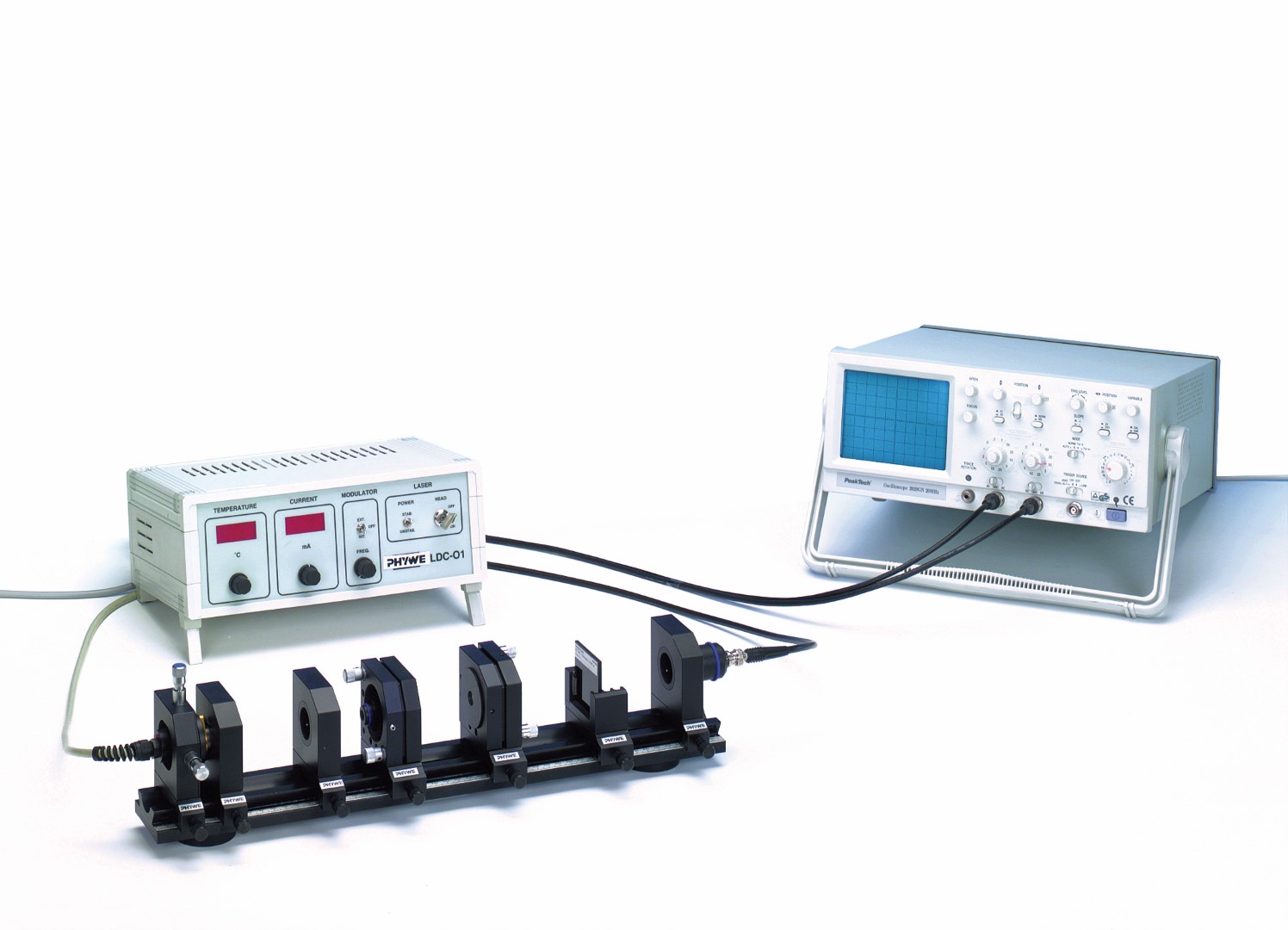
Principle
The rate equation model for an optically pumped four-level laser system is determined. As lasing medium, a Nd:YAG (Neodymium-Yttrium Aluminium Garnet) rod has been selected which is pumped by means of a semiconductor diode laser. The IR-power output of the Nd:YAG laser is measured as a function of the optical power input and the slope efficiency as well as the threshold power are determined. Finally, a KTP-crystal is inserted into the laser cavity and frequency doubling is demonstrated. The quadratic relationship between the power of the fundamental wave and the beam power for the second harmonic is then evident.
Benefits
- Experience the physics of modern solid state lasers
- Get to the point where you turn invisible IR-light into a bright green light
- Find out about the type of relationships that govern different conversion steps
Tasks
- Set up the Nd:YAG laser and optimise its power output.
- The IR-power output of the Nd:YAG laser is to be measured as a function of the pump power. The slope efficiency and the threshold power are to be determined.
- Verify the quadratic relationship between the power of the fundamental wave, with lambda = 1064 nm, and the beam power of the second harmonic with lambda = 532 nm.
Learning objectives
- Optical pumping
- Spontaneous emission
- Induced emission
- Inversion
- Relaxation
- Optical resonator
- Resonator modes
- Polarization
- Frequency doubling