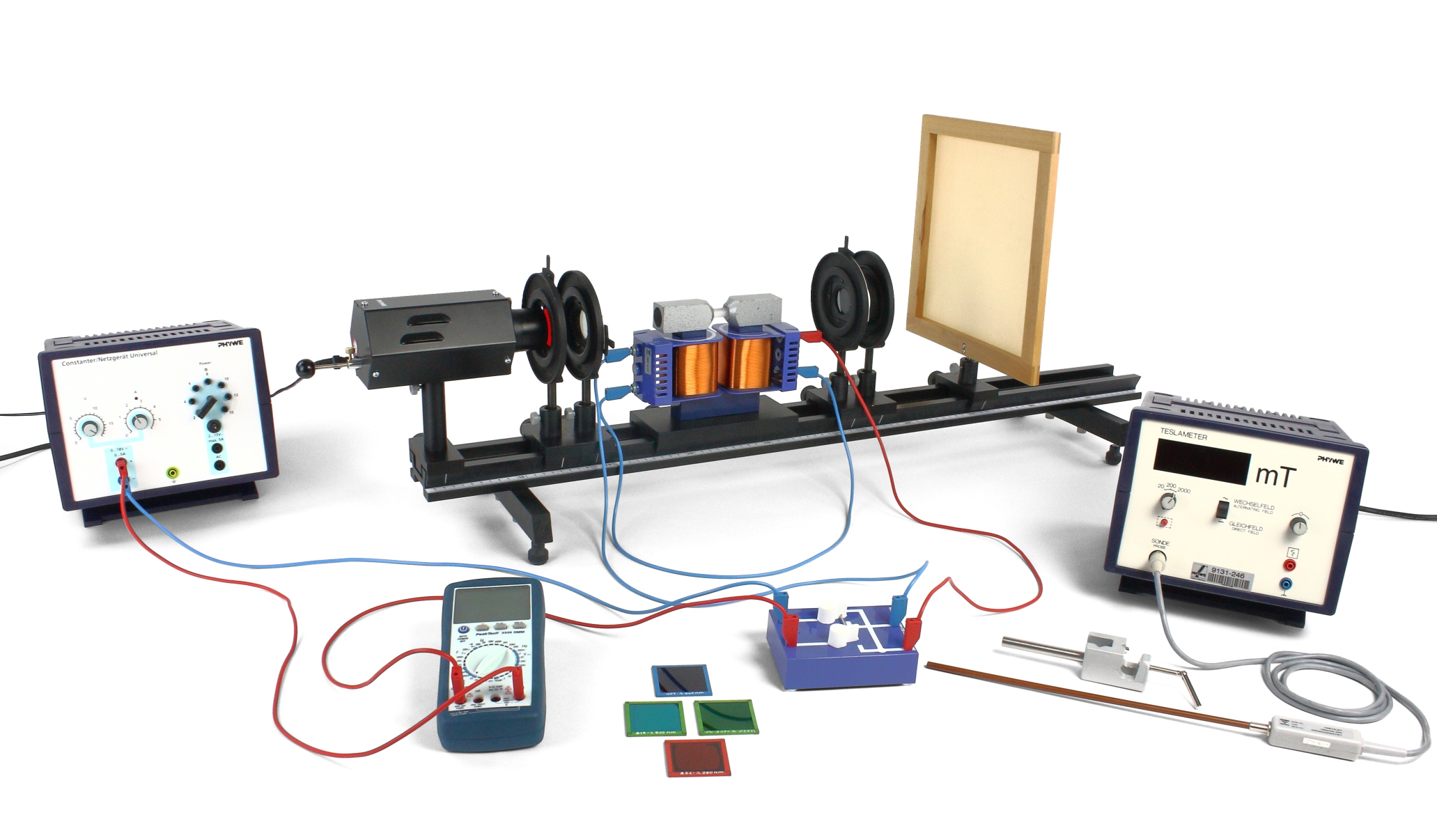
Principle
The angle of rotation of the polarization- plane of plane polarised light through a flint glass rod is found to be a linear function of the product of the mean flux-densitiy and the length of the optical medium. The factor of proportionally, called Verdet's constant, is investigated as a function of the wavelength and the optical medium.
Benefits
- Experience that magnetic fields can influence light by changing its polarization properties
- Learn how wavelength and the optical medium influence the effect of the magnetic field
- Discover a bridge between the fields of optics and electromagnetism
Tasks
- To determine the magnetic flux-densitiy between the pole pieces using the axial Hall probe of the teslameter for different coil currents. The mean flux-density is calculated by numerical integration and the ratio maximum flux-density over mean flux-density established.
- To measure the maximum flux- density as a function of the coil current and to establish the relationship between mean flux-density and coil current anticipating that the ratio found under 1. remains constant.
- To determine the angle of rotation as a function of the mean fluxdensity using different colour filters. To calculate the corresponding Verdet's constant in each case.
- To evaluate Verdet's constant as a function of the wavelength.
Learning objectives
- Electromagnetic field interaction
- Electron oscillation
- Electromagnetism
- Polarization
- Verdet's constant
- Hall effect