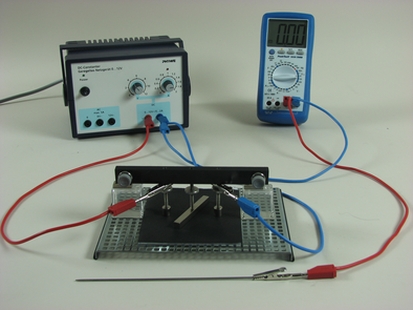
Principle
Investigate how the electric field between two circular electrodes will change, when an electric conductor (here: a rod electrode) is inserted into the field.
Benefits
- No electrolyte required
- Direct measurement of potential with high resistance voltmeter
- Measuring points can be transferred (pressed through) onto a sheet of white paper during measurement
Tasks
- Determine the electric potential of a conductor within an electric field.
- Measure the distribution of electric potential in the electric field between the two electrodes, particularly in the area close to the conductor.
- Derive the electric field pattern.
Learning objectives
With this experiment the students will investigate how the electric field between two circular electrodes changes when an electric conductor (rod electrode) is inserted into the field. The experiment demonstrates that an electric conductor always forms an equipotential surface of an electric field due to shifting of charges. The field lines run perpendicular to its surface.