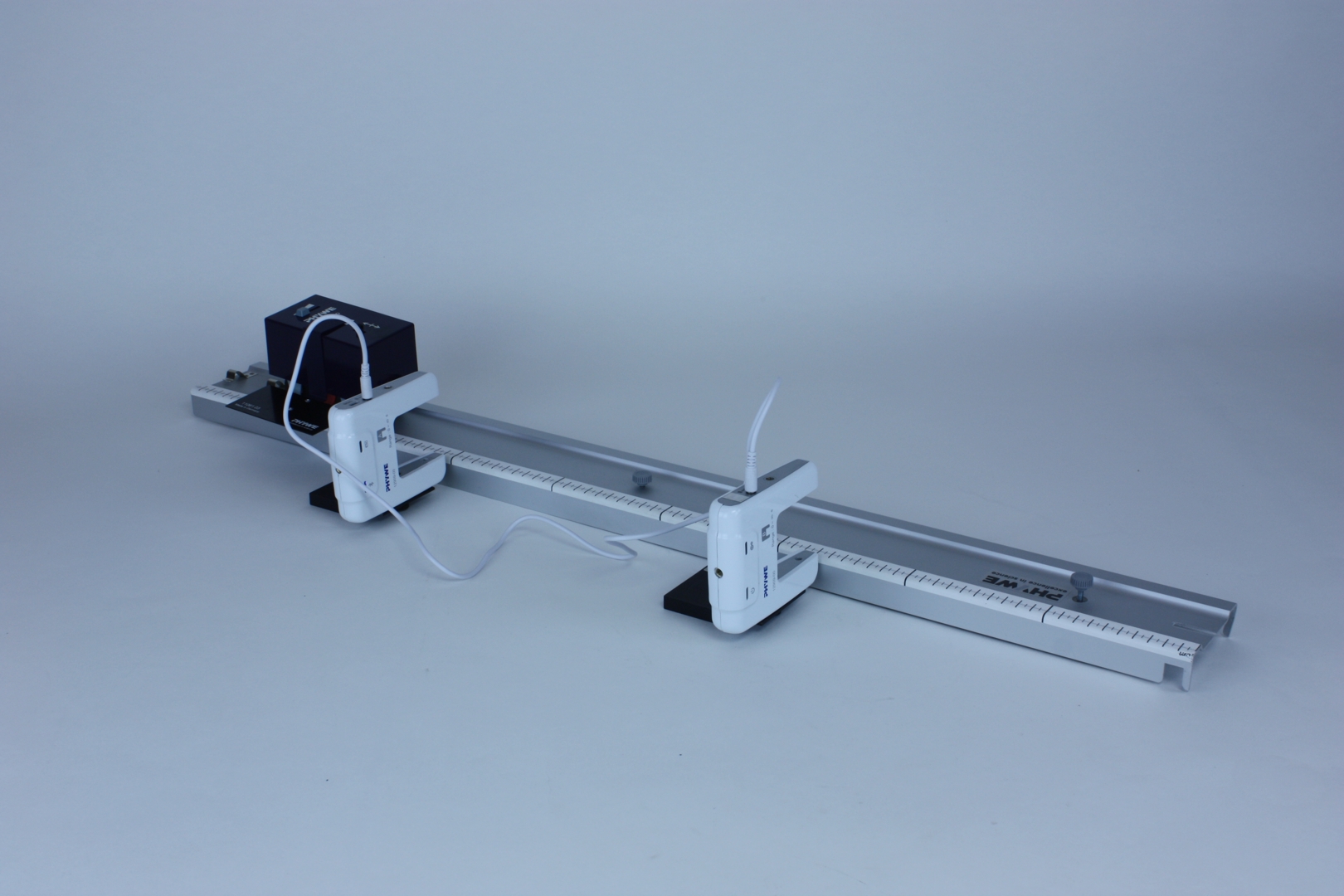
Principle
The measuring carriage with drive travels at constant speed over the carriageway within a measuring series. Accordingly, the same instantaneous and average speeds are always calculated from the measured values.
Benefits
- Especially understandable and didactically prepared description of the experiment (relevance to everyday life, etc.) including protocol questions.
- Future-oriented teaching: Integration into digital science lessons with tablets or smartphones.
- Increased motivation of students by using the intuitive measureAPP.
- Increased media competence.
Tasks
- The students let the measuring trolley with drive run over the road at constant speed. The two light barriers at the edge of the carriageway first measure the time the carriage needs to cover the distance between them. The distance between the light barriers is varied. Then the measuring mode is switched over and the students measure the momentary speed with the rear barrier. Again the position is varied.
- The students each calculate the average or momentary speed (from the length of the shading diaphragm) of the car depending on the location.
Learning objectives
In this experiment the students are to learn more about the laws of motion of uniform rectilinear motion. In particular, the students should become more confident in dealing with the representation of the laws in the form of diagrams. The students should learn to read the acceleration from the velocity-time diagram.