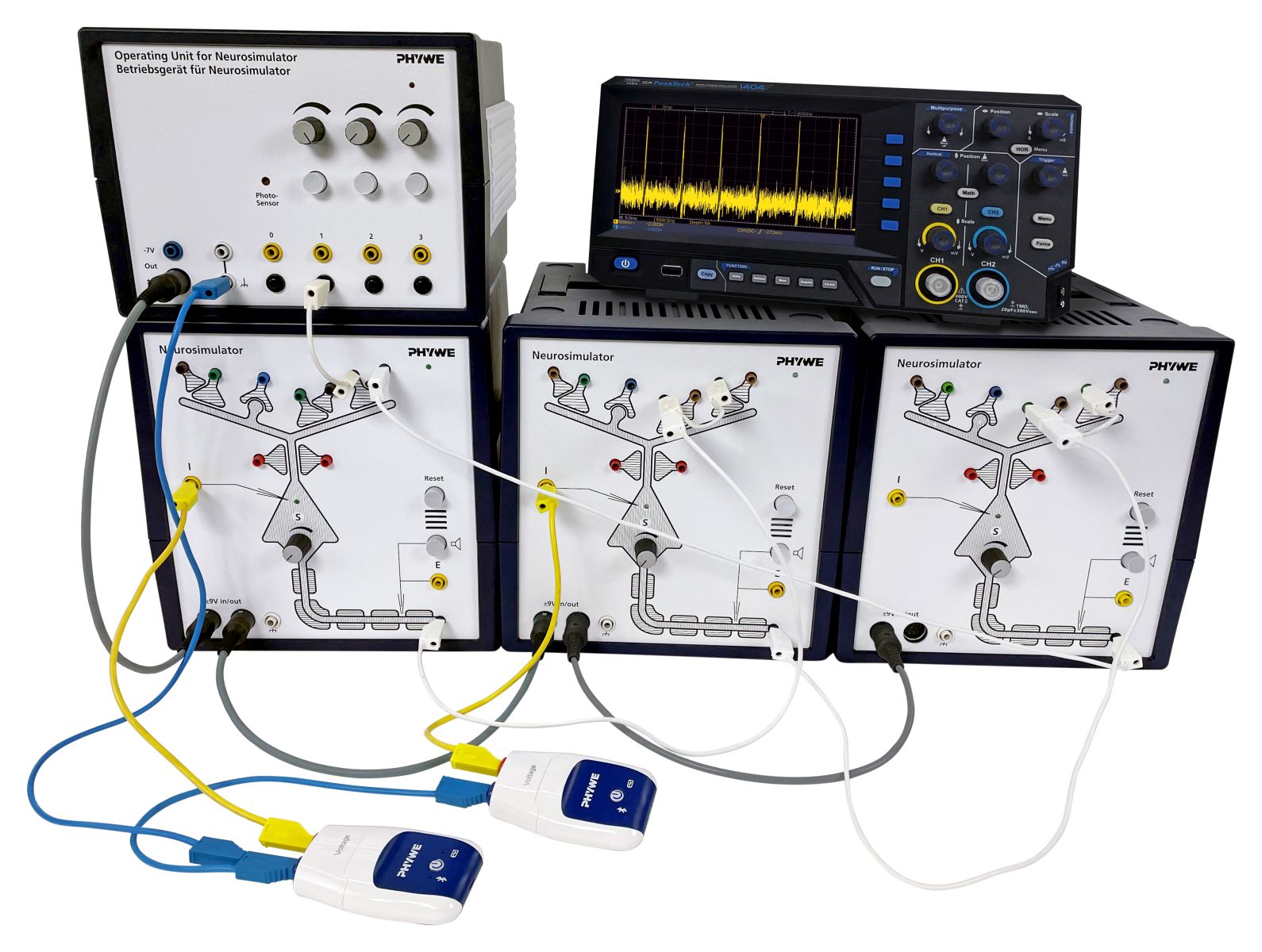
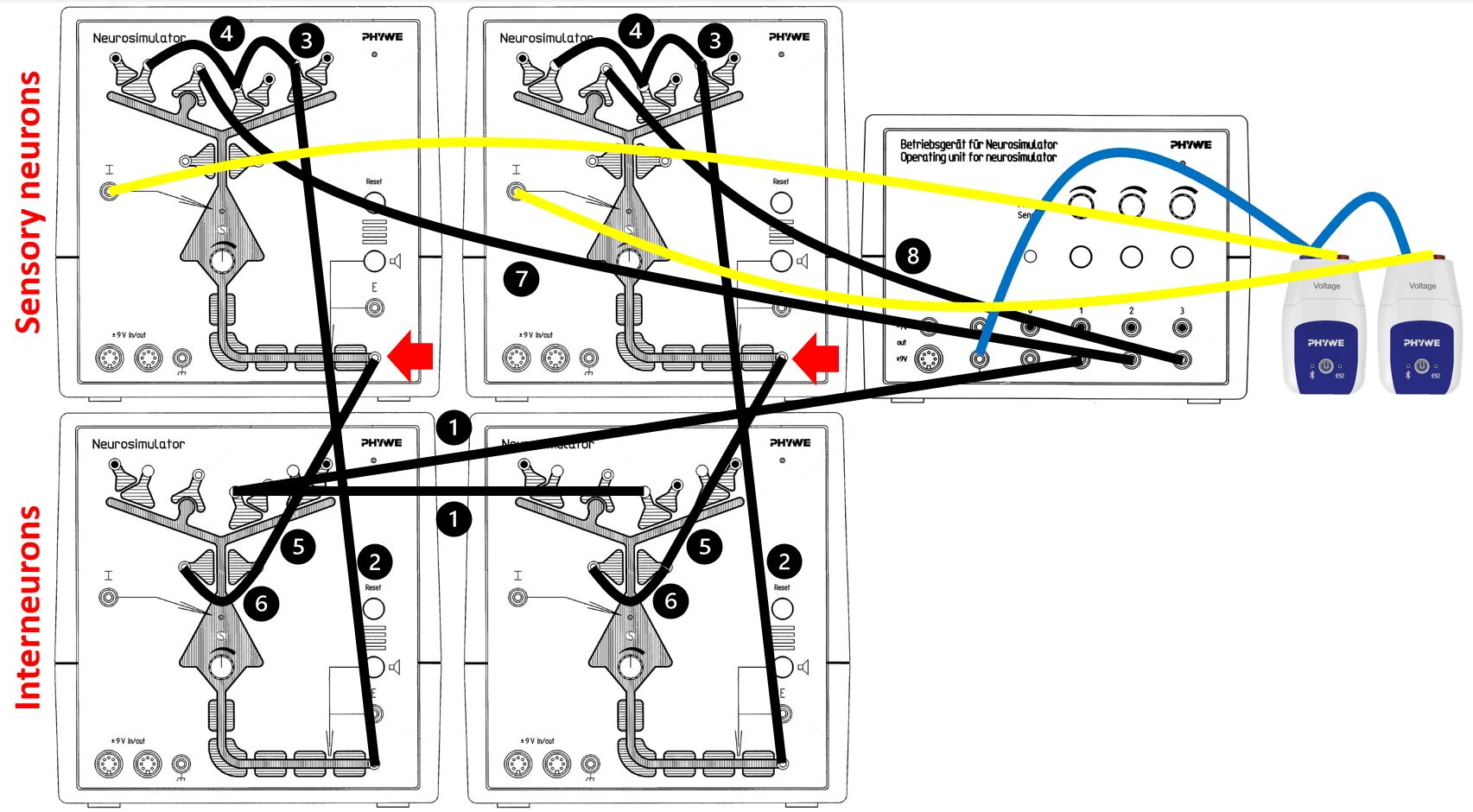
Principle
Interactive learning and teaching system with four neurosimulators for experiments covering nerve cells, nerve cell interactions and neural networks.
Benefits
- Experience processes in the nerve cell, between nerve cells and in neural networks "hands-on"
- Make all properties of a nerve cell easy to understand - action potential, membrane potential, functions of synapses (e.g. synaptic learning and forgetting)
- Discover how nerve cells interact to study the conditioned reflex and synaptic learning
- Switch together three or even four nerve cells to create neural networks to study phenomena like short-term memory
- Ideal for projects at schools and for lab courses in the degree course Neurobiology
Tasks
- When using one nerve cell: use the nerve function model to study the following aspects of a nerve cell: intercellular potential, action potential.
- When using two nerve cells: motoneuron signals with recurrent inhibition by Renshaw cell, motoneuron signals without recurrent inhibition, functional characteristics of Renshaw inhibition, lateral inhibition, contrast improvement, conditioned reflex, reversed stimulus succession does not bring about a conditioned reflex.
- When using three nerve cells: transient (phasic) responses: focus on visual sense, body clock, short-term memory, special anatomical circuits: cerebral cortex and sensoric learning, functional characteristic of a triad.
- When using four nerve cells: direction selectivity by unilateral inhibition, self-calibration of paired sensory channels.
Learning objectives
- When using one nerve cell: comparison between low and high threshold and stimulus levels, membrane time constant and low pass filtering, low-pass filtering, excitatory synapse, depolarisation, temporal summation, spatial summation, synaptic amplification by terminal branches, effect of decreasing stimulus, Hebbian synapse, synaptic learning and forgetting, inhibitory synapse, hyperpolarization, spacial inhibitory-excitatory summation, veto synapse.
- When using two nerve cells: lateral inhibition, contrast improvement, nerve cell interaction, conditioned reflex, Renshaw inhibition, motoneuron.
- When using three nerve cells: neuronal oscillator, rotating excitation, cerebral cortex and sensoric learning, triad.
- When using four nerve cells: unilateral inhibition, self-calibration of paired sensory channels, nerve cell interaction, neural network, ganglion cell, axon, interneuron.
Incl. data acquisition system Cobra SMARTsense for mobile devices (iOS and Android) and for Windows. Incl. oscilloscope for action potential measurements.
Recommended accessories
With these accessories you can generate real added value